The Rise of Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
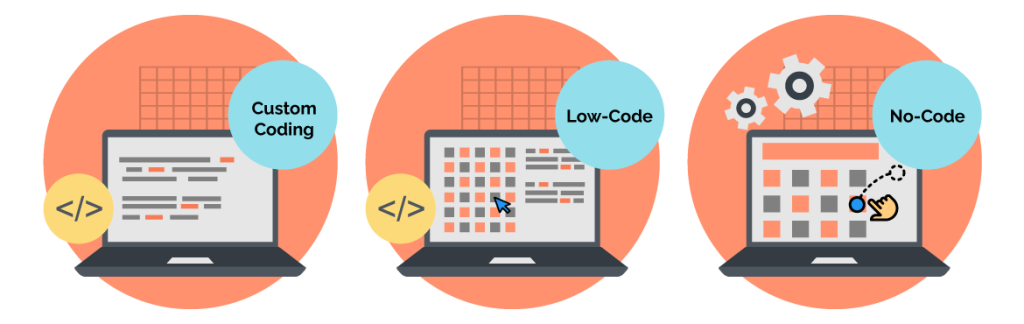
The rise of low-code and no-code platforms is transforming the software development landscape. These platforms revolutionize how applications are built, enabling individuals and organizations to create software with minimal or no traditional coding. By offering visual interfaces, drag-and-drop functionality, and prebuilt modules, low-code and no-code platforms democratize software development and accelerate the delivery of business solutions.
In an era where digital transformation is critical for business success, the ability to rapidly develop and deploy applications can be a competitive advantage. From startups to large enterprises, organizations are embracing low-code and no-code platforms to reduce development time, lower costs, and empower non-technical users to participate in application creation. This article explores the evolution, current innovations, future trends, challenges, and implications of low-code and no-code platforms in modern software development.
Understanding Low-Code and No-Code Platforms: Rise of Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
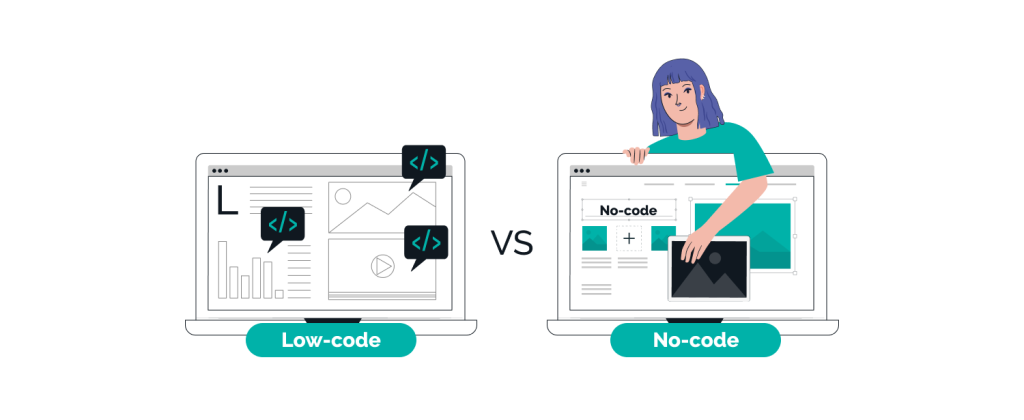
What Are Low-Code Platforms? Understanding the Rise of Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
Low-code platforms provide a visual development environment that allows developers to design applications using drag-and-drop components, prebuilt templates, and automation tools. While some coding may still be required for complex functionality, low-code platforms significantly reduce the need for extensive manual programming.
Low-code platforms cater to professional developers looking to accelerate project delivery, streamline workflows, and maintain control over custom code when necessary. They bridge the gap between traditional development and rapid application deployment, offering scalability and flexibility for enterprise applications.
What are No-Code Platforms?
No-code platforms, on the other hand, enable individuals without any programming knowledge to build applications entirely through visual interfaces. Users can create functional apps, workflows, and integrations without writing a single line of code.
No-code platforms empower business users, citizen developers, and entrepreneurs to translate ideas into working applications quickly. By eliminating the technical barrier, no-code platforms facilitate innovation, improve agility, and reduce dependency on IT departments.
Key Features of Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
- Visual Development Interfaces: Drag-and-drop builders simplify the creation of user interfaces, workflows, and logic.
- Prebuilt Templates and Modules: Reusable components accelerate development and ensure consistency.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless connections with APIs, databases, and third-party services enable complex functionality.
- Automation and Workflow Tools: Built-in automation streamlines repetitive tasks and operational processes.
- Scalability and Security: Enterprise-grade low-code platforms provide secure environments and support large-scale applications.
Together, these features make low-code and no-code platforms essential tools for modern software development, reducing time-to-market and expanding the pool of potential developers.
The Evolution of Low-Code and No-Code Platforms: Driving the Rise of Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
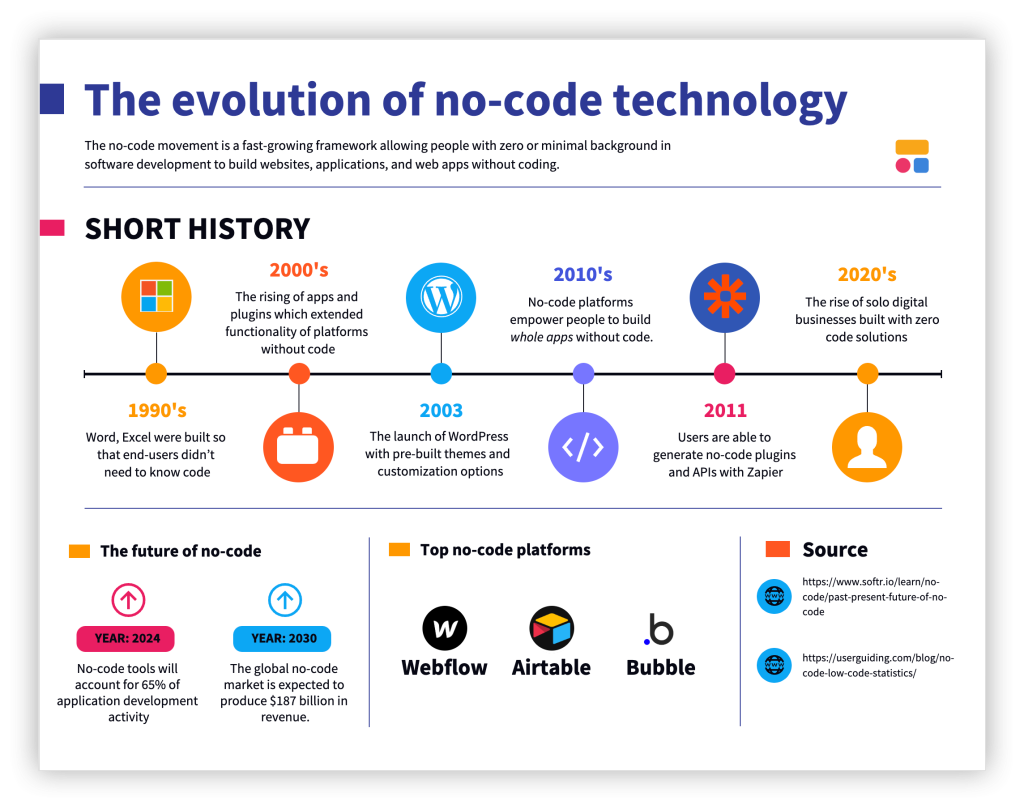
Early Visual Programming Tools in the Rise of Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
The origins of low-code and no-code platforms can be traced back to early visual programming environments such as Microsoft Visual Basic and HyperCard in the 1980s and 1990s. These tools introduced the concept of building applications through visual interfaces rather than manual coding, laying the foundation for modern low-code platforms.
Rise of Rapid Application Development (RAD) with Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
In the 2000s, rapid application development (RAD) methodologies emphasized iterative development, prototyping, and user feedback. RAD tools incorporated visual modeling, reusable components, and simplified deployment, allowing developers to create applications faster than traditional approaches.
Modern Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
The last decade has seen the emergence of modern low-code and no-code platforms like OutSystems, Mendix, Appian, and Bubble. These platforms leverage cloud infrastructure, AI-powered automation, and integration with enterprise systems to deliver sophisticated applications quickly.
The evolution of low-code and no-code platforms reflects the growing need for speed, accessibility, and collaboration in software development. Organizations now have the tools to empower both professional and citizen developers to build applications efficiently.
Key Innovations in Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
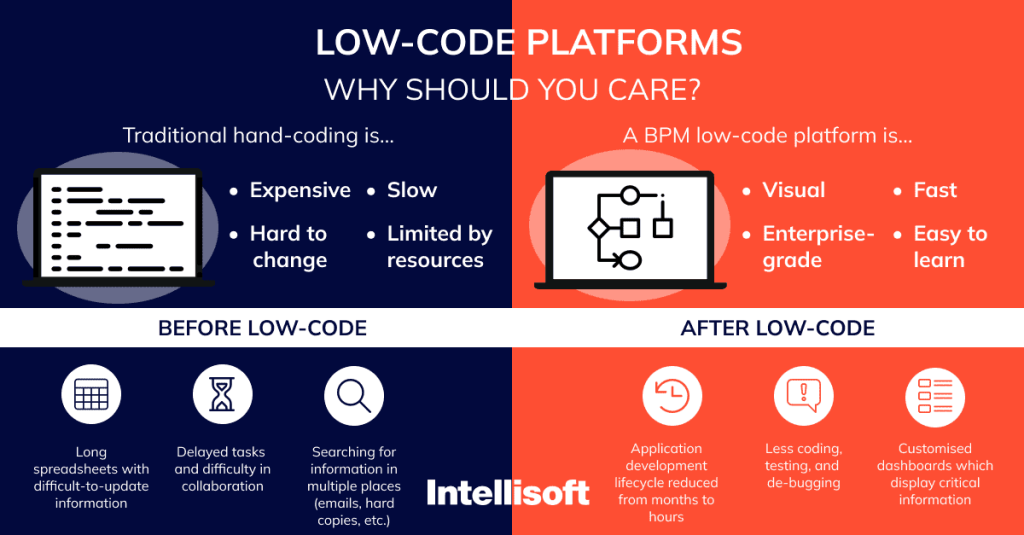
AI-Powered Development Assistance
Modern platforms incorporate AI to assist in application design, code generation, and testing. AI algorithms can suggest workflows, optimize user interfaces, and even generate backend logic, reducing manual effort and improving application quality.
Prebuilt Integrations and API Connectors
Low-code and no-code platforms provide extensive libraries of prebuilt integrations, enabling seamless connectivity with cloud services, databases, and third-party applications. This innovation accelerates development and reduces the complexity of building connected applications.
Advanced Workflow Automation
Automation tools within these platforms allow users to design complex workflows that handle business processes efficiently. Features like conditional logic, triggers, and scheduled tasks enable the creation of intelligent, self-managing applications without coding.
Collaborative Development Environments
Low-code and no-code platforms support collaborative development, allowing teams of developers, designers, and business users to work together in real-time. Version control, access management, and collaboration tools enhance productivity and reduce development errors.
Cloud-Native and Scalable Architecture
Most modern platforms are cloud-native, offering scalable infrastructure, automated deployment, and high availability. Applications built on cloud-native low-code and no-code platforms can grow with business needs, supporting global users and high transaction volumes.
Low-Code and No-Code Platforms in Business

Digital Transformation
Organizations leverage low-code and no-code platforms to accelerate digital transformation initiatives. By enabling rapid application development, these platforms help businesses adapt to changing market conditions, streamline operations, and improve customer engagement.
Citizen Developers and Empowerment
One of the most significant impacts of no-code platforms is the empowerment of citizen developers. Business users can create applications to address specific operational challenges without waiting for IT resources, increasing innovation and reducing bottlenecks.
Cost Reduction and Time Efficiency
By minimizing manual coding, low-code and no-code platforms reduce development costs and shorten project timelines. Organizations can deliver high-quality applications faster, achieving a higher return on investment.
Use Cases Across Industries
- Healthcare: Patient management, appointment scheduling, and telemedicine platforms.
- Finance: Automated reporting, loan processing, and compliance applications.
- Retail: Inventory management, order tracking, and personalized customer experiences.
- Education: Learning management systems, student tracking, and online collaboration tools.
These examples illustrate how low-code and no-code platforms are transforming industries by making software development faster, more accessible, and more aligned with business needs.
Future Trends in Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
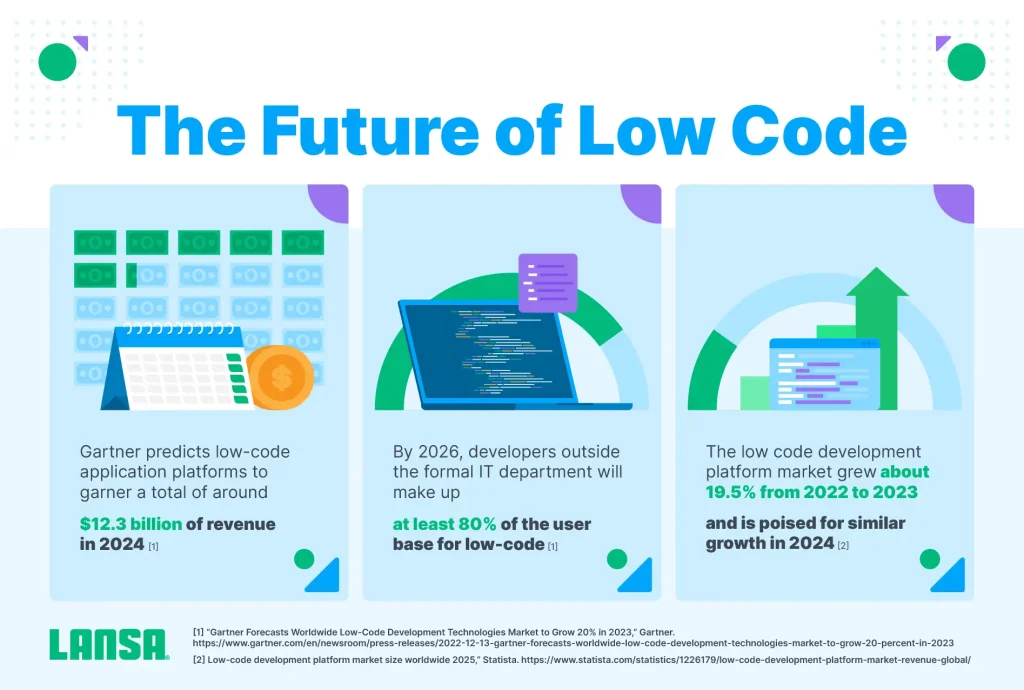
AI-Enhanced Application Development
Future platforms will integrate AI more deeply, offering predictive suggestions, automated testing, and intelligent error correction. AI-driven development will further reduce time-to-market and improve application quality.
Integration with IoT and Edge Computing
Low-code and no-code platforms are expanding to support IoT and edge computing applications. Users will be able to build connected devices, monitor data streams, and deploy edge applications without deep technical expertise.
Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation combines AI, machine learning, RPA (Robotic Process Automation), and low-code/no-code platforms to automate complex business processes end-to-end. Organizations will increasingly adopt these solutions to enhance operational efficiency and agility.
Multi-Experience Development
Future platforms will focus on multi-experience development, enabling applications that work seamlessly across web, mobile, wearable devices, and immersive environments like AR/VR.
Democratization of Software Development
Low-code and no-code platforms will continue to democratize software development, empowering more individuals to contribute to digital innovation. This trend will expand the talent pool, foster creativity, and accelerate the pace of technological progress.
Challenges and Considerations

Security and Compliance
As more non-technical users develop applications, ensuring security and regulatory compliance becomes crucial. Platforms must provide robust access control, encryption, and auditing capabilities to protect sensitive data.
Complexity Limitations
While low-code and no-code platforms handle most use cases, highly complex or specialized applications may still require traditional coding. Developers must assess platform limitations before committing to large-scale projects.
Vendor Lock-In
Some platforms may create dependency on proprietary tools, making migration or integration with other systems challenging. Organizations should evaluate vendor flexibility and standards compliance.
Skill Gap and Training
Although no-code platforms reduce the need for programming knowledge, users still need training in platform features, best practices, and design principles to create effective applications.
Governance and Oversight
The proliferation of citizen-developed applications can lead to shadow IT and fragmented systems. Organizations need governance frameworks to manage application quality, security, and scalability.
Conclusion
The rise of low-code and no-code platforms is reshaping the software development landscape. By enabling rapid application development, empowering non-technical users, and integrating AI-driven tools, these platforms are accelerating digital transformation across industries.
The future of software development will increasingly rely on low-code and no-code platforms, offering faster delivery, greater accessibility, and multi-experience capabilities. While challenges like security, complexity, and governance remain, the benefits of democratized software creation are undeniable.
Organizations and developers embracing these platforms can innovate faster, respond to changing business needs, and deliver high-quality applications without the traditional barriers of manual coding. Low-code and no-code platforms are not just tools—they are a paradigm shift in how software is developed, deployed, and experienced.